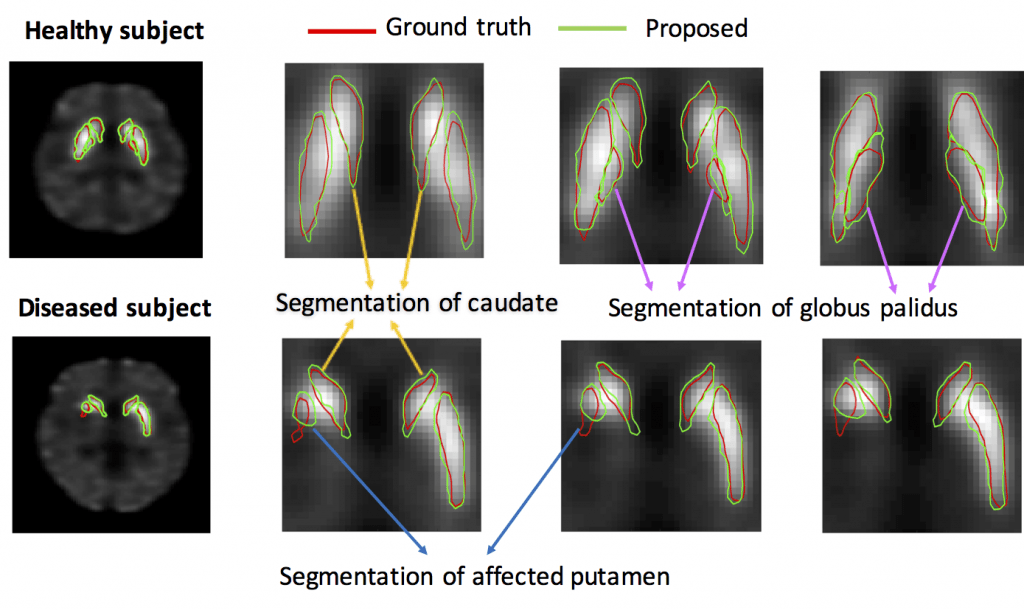
Regional dopamine transporter (DaT) uptake in sub-cortical regions, as derived from DaT single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) images, may help provide markers to measure severity of Parkinson disease. However, to achieve this goal, there is a need for methods to reliably reconstruct, segment, and then quantify these uptakes from different regions in DaT-SPECT images. To address this need, we developed ESegNet, a novel deep-learning-based techniques to segment caudate, putamen and globus pallidus from SPECT images. These regions are very small, and the globus pallidus in particular, is visually impossible to demarcate in SPECT images. However, these regions can be observed on MR images. We developed an approach that could transfer this knowledge learned from MR images to delineate SPECT images.
References:
Z. Liu, H. Moon, R. Laforest, J. Perlmutter, S. A. Norris, A. K. Jha, “Fully automated 3D segmentation of dopamine transporter SPECT images using an estimation-based approach”, (arxiv)
H.S. Moon, Z. Liu, M. Ponisio, R. Laforest, and A. K. Jha, A physics-guided and learning-based estimation method for segmenting 3D DaT-Scan SPECT images. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 61(supplement 1), pp.10-10, 2020 (selected for Young Investigator Symposium, Highest scored abstract in the Data Sciences category) (link)
M. A. Rahman, R. Laforest, A. K. Jha, “A list-mode OSEM-based attenuation and scatter compensation method for SPECT”, IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2020 (link)
Z. Yu, M. A. Rahman, A. K. Jha, “A Transmission-less Attenuation Compensation Method for Brain SPECT Imaging”, IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2020